Homes Incorporated: Offshore Ownership of Real Estate in the U.K.
Abstract
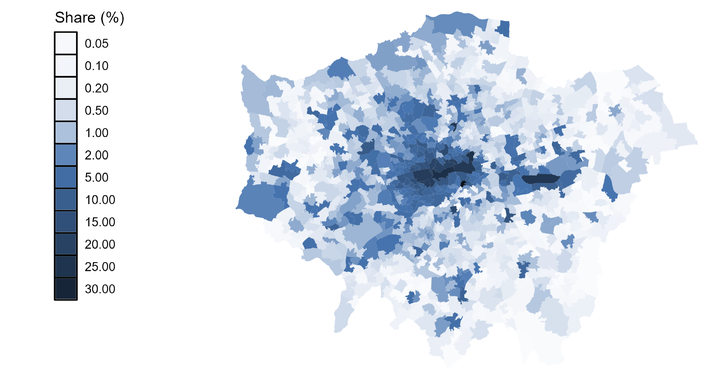
This paper studies offshore ownership of residential real estate in the United Kingdom. Drawing on administrative land records, property transaction data, multiple offshore leaks and a global firm database, we present three main findings. First, ownership through offshore tax havens is economically significant with a market share of 1.5% overall and around 15% for top-end properties. Second, both tax and disclosure rules shape patterns of offshore ownership, suggesting that tax avoidance and secrecy are important motives for the beneficial owners. Third, the drop in offshore demand following the Brexit referendum caused prices and vacancy rates to fall, suggesting that offshore ownership has real effects in housing markets by inflating prices and lowering utilization of the housing stock. Our IV estimates imply that a change in offshore property demand equivalent to 1% of total property demand changes property prices by around 1.3%.